
This guide will show how to use CRM to forecast revenue and sales efforts. By the end, you’ll know the features that make forecasting easy.
Forecasting where your organization will be in the future helps you anticipate incoming challenges.
SMBs that find success nowadays take measures to analyze past, current, and future metrics with the help of CRM.
If you’re experiencing a lack of company predictability, this guide on CRM forecasting is just what you need to anticipate future numbers without complication.
Table of Contents:
- What Is CRM Forecasting?
- 3 Problems SMBs Struggle With That CRM Forecasting Solves
- How To Forecast Using CRM Step-By-Step
- Best Practices When CRM Forecasting
- A Final Wrap-Up Of CRM Forecasting’s Value

VipeCloud is the only Automation tool your small business needs to
be the hero to your customers.
With Email, Texting, Social, Suites, Chat, Stories, Video Email & Sign Up Forms fully built-in, we provide you with the perfect platform to grow your business.
15 Day Free Trial – Get started risk free. No CC needed.
What Is CRM Forecasting?
CRM forecasting is when CRM analytics are used to predict future metrics and business outcomes.
Forecasting using CRM helps you to compile all the business information you need for an adequate analysis.
Forecasting without this critical data can be a recipe for missing information and even lacking context.
For this reason, SMBs need CRM for better forecast accuracy.
And it’s this accuracy that prevents future events from thwarting organizational plans and goals.
For instance, how often is revenue projected to be a certain amount and ends up falling short of expectations?
Sales forecasting using CRM can help you factor in sales velocity, number of opportunities, and pipeline value to increase the likelihood of the correct prediction.
There are also team activity metrics to help pinpoint if day-to-day actions are in line with revenue goals.
3 Problems SMBs Struggle With That CRM Forecasting Solves
If you’re experiencing these problems, CRM forecasting may be your best fix.
1. You Struggle To Manage Cash Flow
Cash flow is king for small businesses since it allows you to reinvest consistently, store funds for a rainy day, or expand your team.
If cash flow seems to be a struggle, you may need to improve how your numbers are forecasted.
This is especially the case if you see inconsistent revenue.
Implementing CRM can help you see all your current and potential deals and their value in one place.
You can also track the speed at which you’re selling to ensure cash flow is where it needs to be.
2. You Spend Too Much On Unnecessary Costs
The ideal expenses for your organization should help you make more revenue.
Think of things like software, partnerships, team members, etc.
The costs to avoid are those that don’t provide value to your business, i.e., unnecessary, miscellaneous expenses.
CRM partnered with accounting software can help you track your business balance sheet, so you know your overhead expense, the revenue coming in, and profit margins.
Once you know these?
Sales forecasting becomes much easier.
3. You Don’t Know Your Predicted Revenue

Less than 50% of sales leaders are confident in their ability to forecast revenue accurately.
Predicted revenue should be an estimation that is as accurate and clear as possible.
If you don’t have a predicted revenue number in mind, it’s a sign to take steps toward forecasting.
You predict revenue by taking your current and past sales metrics to calculate future revenue.
How To Forecast Using CRM Step-By-Step
Let’s go over how to forecast revenue for your business using CRM and forecasting fundamentals.
1. Know Your Past Numbers
Begin your CRM forecasting process by identifying how much revenue you typically generate in a month, quarter, or year.
What do your past sales metrics look like, and why are they so?
This is best done using a CRM reporting tool like VipeCloud Reports, where you gain a top-down view of sales revenue and filter it by timeframe.
Here are metrics to look for other than sales revenue:
- Average close rate
- CLV
- Churn rate
- Average pipeline value
- Average sales cycle length
- Sales activity data
2. Know Your Current Numbers
Next, factor your numbers now into those you’ve gathered from the past. Doing this will help you estimate what next month or quarter numbers will look like.
Be sure to evaluate the same metrics as you did when locating your past numbers.
Using past and present metrics to pinpoint future numbers is known as predictive modeling.
After having this clarity, it’s time to make a note of data outliers.
3. Consider Outliers That Effect Data
Before making conclusions from your two data sets, consider outside factors influencing that information.
For instance, maybe prior revenue spikes were due to a rockstar marketing strategy you implemented.
However, now, that marketing strategy isn’t as viable, which has caused less revenue growth.
Another scenario could be things that are harder to control, such as staff resignations, seasonal market demand changes, etc.
Think about researching market trends which can be a suitable way to pinpoint how your industry performs during certain times of the year.
4. Make Revenue And Sales Predictions
With all the information you have gathered (including market trends), make predictions on the timeframe you’re forecasting.
Talking over predictions with fellow stakeholders is also vital to ensure everyone’s on the same page.
5. Consider What Would Make The Numbers Better
With your projected numbers in place, what can you do to improve them?
For example, if you forecasted that you’d get 25 discovery calls next month, what could be done to turn that into 40 discovery calls?
You could consider adding more sales enablement tools to nurture more leads or a new marketing avenue like email marketing to land more appointments.
If your goal is to increase your lead conversion rate by X% next quarter, you can adopt a sales playbook or methodology to make that happen.
One of the fundamental aspects of this step is evaluating your sales process since that’s what creates your results (numbers) in the first place:
- Where are prospects dropping off, and why?
- How are you increasing the AOV of a given customer?
- How are you increasing CLV?
- Should you increase the price of your product or not?
This makes CRM pipelines so valuable – their ability to give accurate sales data details via your sales pipeline.
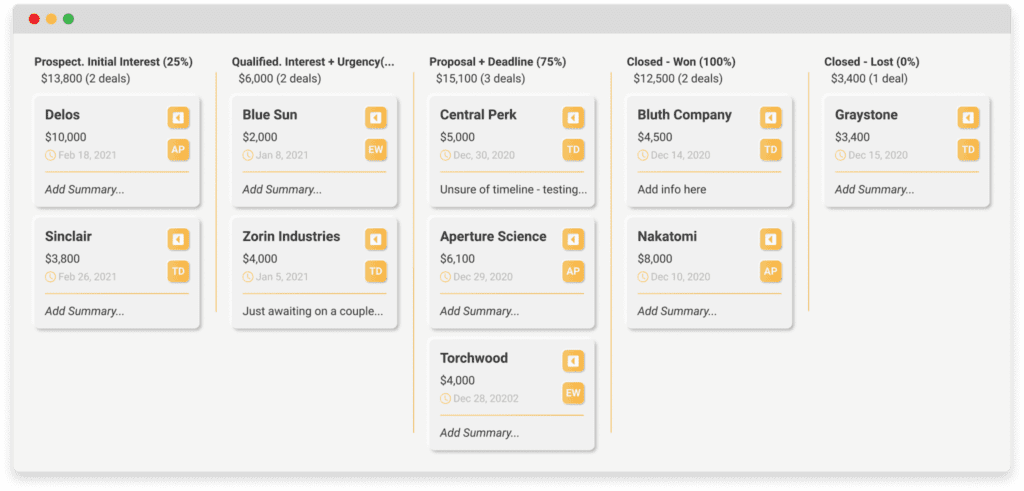
6. Consider What Could Make Numbers Worse
Could your future numbers worsen if changes aren’t made?
Sometimes numbers based on the past and present are due to certain factors being in place.
However, if those deciding factors disappear, your numbers may suffer more.
For instance, if the majority of your company revenue comes from 2 clients, and 1 decides to cancel, that could mean disaster.
Once you factor this in, you can take action in different ways:
- Increasing the average order value of your smaller accounts
- Giving bigger clients incentives to remain loyal (besides delivering them an excellent product or service)
- Offering retainer contracts that last specific timeframes
Anticipating your “black swan” events (though seemingly unlikely to happen) is an excellent way to add more stability to revenue, especially as an SMB.
7. Set KPI Goals To Improve Your Numbers
KPIs help steer your organization towards a goal.
If your projected numbers next month are drastically different from what you thought earlier in the year (KPI), consider adjusting that goal.
This helps make it attainable, which is one of the pillars of the SMART goals formula:
- Specific
- Measurable
- Attainable
- Relevant
- Time-based
Attainable goals are not only most likely to be reached but can drive success momentum.
4 Best Practices When CRM Forecasting
1. Don’t Forecast Too Far Ahead
Forecasting too much into the future may hinder accuracy since predicting things at play is harder.
Sure, larger organizations can do so since they have decades (if not centuries) of data to reference.
But as an SMB, with just a handful of years at play, forecasting up to 24 months may be more ideal.
This also may depend on your industry verticle, business pay structure, and other factors.
2. Weigh Best And Worst-case Scenarios
Identifying your forecast’s best and worst-case scenarios can help you prepare for them.
The major client loss example mentioned earlier is a perfect example of this. Look to create contingency plans for worst-case scenarios and review them with stakeholders.
It also helps to hedge worse-case scenarios to minimize risk.
Hedging these scenarios simply means having a plan that smoothens them when they happen.
For example, a SaaS company may use a support partner if its user base grows faster than anticipated. This partner can support the capacity, preventing scaling issues.
3. Improve Upon Forecasting Itself
Just like many business skill sets, sales forecasting can always be improved upon.
You can cross reference past forecasting efforts you’ve made and learn valuable lessons from them.
Since CRM is a significant part of forecasting, improving your CRM is just as valuable.
Consider how good of a fit the analytics are for your organization.
For example, finding that the reporting tools of your CRM are limited? It could be a sign to possibly upgrade your plan or use a CRM with better reporting and sales forecasting capabilities.
4. Improve Qualification Using Better Sales Methodologies
Earlier, we talked about how the sales process directly correlates to the quality of your metrics.
The qualification stage of your sales process sets the tone for who enters your pipeline and how well prospects convert.
If you want future conversion percentages to align with your goal, then making your qualification stage effective is an important step.
Consider implementing a sales methodology (or an improved one) help you identify ideal customers.
Here are sales methodologies you can experiment with and implement:
- SNAP Selling – Keep it simple, be invaluable, always align, raise priorities
- SPIN Selling – Situation, problem, implication, need-payoff
- BANT Selling – Pinpointing budget, authority, need, timeframe
- Challenger Selling – Educating prospects first, building credibility, and positioning your product as the ideal solution
Start CRM Forecasting With VipeCloud
CRM forecasting’s role is to streamline how you determine future numbers.
In other words, it’s about making your forecast more accurate without complicating it.
This is what VipeCloud does with its Sales and marketing Suite.
As a VipeCloud user, you can access simple-to-use tools for forecasting, team management, marketing, and more.
Want to learn more?
Request a demo, and an expert will walk you through the CRM and its capabilities.
There’s also a 15-day free trial with your name on it when you sign-up today.
CRM Forecasting FAQ
CRM forecasting is the process of predicting future sales, revenue, or other business outcomes based on historical data and current trends within a customer relationship management system.
You can use various factors such as historical sales data, customer behavior patterns, market trends, and predictive analytics models to predict potential revenue in CRM.
From our experience, the accuracy of forecasting methods varies depending on the context and industry. However, we’ve found that techniques like time-series analysis and machine learning algorithms can be particularly effective when applied correctly.




Leave a Comment